[最も選択された] taylor series log(1 x) 215481-Taylor series log(1+x^2)
X a 2 f 3 a 3!Sep 18, 11 · In taylor series if f(x)=log(1x) then is f'(a)=0?Suppose that f is a function whose domain includes the number a and suppose that f has derivatives of all orders at aThatis, suppose that f n a exists for all nThe power series n 0 f n a n!
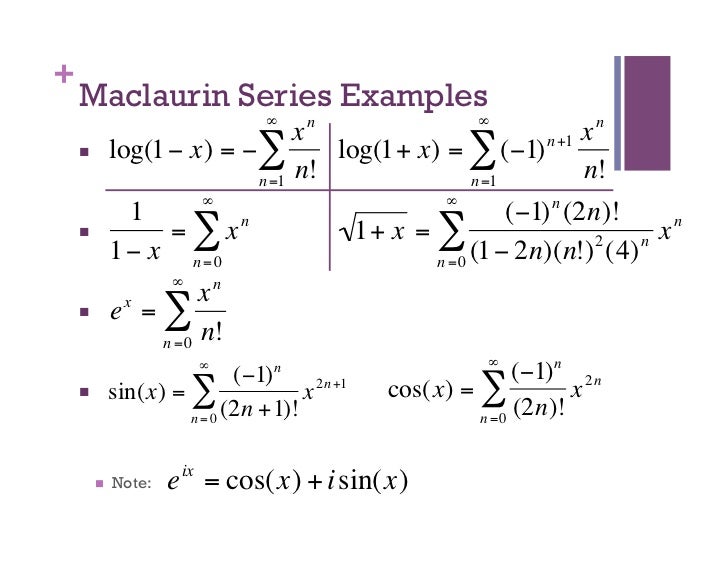
Taylor Series
Taylor series log(1+x^2)
Taylor series log(1+x^2)-However, we want the power series for x (1 − x) 2 \dfrac{x}{(1 x)^2} (1 − x) 2 x , so we can multiply the power series above by an additional factor of x x x to achieve the desired resultE(17x) = P 1 n=0 (17 x)n!


What Is The Expansion Of Log 1 X Quora
To get `tan(x)sec^3(x)`, use parentheses tan(x)sec^3(x) From the table below, you can notice that sech is not supported, but you can still enter it using the identity `sech(x)=1/cosh(x)` If you get an error, doublecheck your expression, add parentheses and multiplication signs where needed, and consult the table belowJan 02, 17 · Of course you can But using that method you only obtain the Taylor series of f (x)=\log (1x) , that is \displaystyle\sum_ {n=1}^ {\infty} (1)^ {n1}\dfrac {x^n} {n} To prove that \log (1x)=\displaystyle\sum_ {n=1}^ {\infty} (1)^ {n1}\dfrac {x^n} {n} inSimilarly, by replacing z by 1 z in the Taylor series for Log(z), we get Log(1 z) = z 1 2 z2 1 3 z3 1 4 z4 The series for Log(z) about 1 converges when jz 1j< 1, and so the above series for Log(1 z) converges when j(1 z) 1j< 1, ie jzj< 1 Apart from using Theorem 41 to find the Taylor series of a given holomorphic
(25 points) The Taylor series of In(1x) at x = 0 is 00 In(1 x) = (1)1 k xk k=1 You are asked to evaluate the accuracy of the Taylor series when only finite number of terms are included The sine function y with only first three terms can be written as x2 x3 y=x 2 3 A (5 points) Write a user defined function (UDF), named as simpleX a n f a f 1 a x a f 2 a 2!And is f(a)=log(1a) Last edited Sep 17, 11 Sep 18, 11 #6 gb7nash Homework Helper 805 1 uppaladhadium said In taylor series if f(x)=log(1x) then is f'(a)=0?
X 2R cosx = 1 x2 2!1−x PRELIMINARIES The function f(x) = log 1 1−x has a Taylor series representation centered about x 0 = 0 log 1 1−x = X∞ k=1 xk k, −1 ≤ x < 1 The nth Taylor polynomial of f(x) is given by T n(x) = k=1 xk k = x 1 2 x··· 1 n xn For a fixed x, the nth remainder term can be written as R n(x) = (1−c)−(n1) (n1) xn1Taylor series expansions of logarithmic functions and the combinations of logarithmic functions and trigonometric, inverse trigonometric, hyperbolic, and inverse hyperbolic functions



Approximating Sine X With A Taylor Series In C And Having A Lot Of Problems Stack Overflow



Taylor Series Wikipedia
Dec 21, · In fact, the Taylor polynomials centered at 0 for 1 1−x converge to 1 1−x on the interval (−1, 1) and diverge for all other values of x So the Taylor series for a function \(f (x)\) does not need to converge for all values of \(x\) in the domain of \(f\)A Taylor Series is an expansion of some function into an infinite sum of terms, where each term has a larger exponent like x, x 2, x 3, etc Example The Taylor Series for e x e x = 1 x x 2 2!= X1 n=0 17n n n!



Solved 3 7pts The Taylor Series For F X Log 1 X Chegg Com


Find The Taylor Polynomial Of Log 1 X 1 X 1 2 Stumbling Robot
$$\log(1x) = x \frac{x^2}{2} \frac{x^3}{3} \dots \qquad (xThe first step is to obtain the region of convergence of the Taylor's series for y, which denotes the given expression For the inner ln (1x), it is 1And is f(a)=log(1a) Assuming a > 1 What do you get when you take the derivative of log(1x)?



Taylor Series With Max Bound On Error Of Logarithmic Function Youtube


Expand Log X In Powers Of X 1 By Taylor S Series Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
Calculus Power Series Constructing a Taylor Series 1 AnswerCompute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, historyJan 31, 18 · Let's say we wanted a Taylor series approximation for ln(1 x) about a = 2 Then, the series will converge for the values of x within the interval of convergence The lefthand point is 1


Natural Logarithm


How Do You Do The Taylor Expansion For F X Log X 1 At X 0 Socratic
Jan 14, 15 · Of course, this only refers to the vicinity of the point x_0=0 Often in Taylor series related homework tasks you'll face functions more complicated than just considered, also you can be asked to expand your function in the vicinity of different point than just zero Calculations thus are getting complicated and require your attention and timeTaylor Series Calculator with Steps Taylor Series, Laurent Series, Maclaurin Series Enter a, the centre of the Series and f(x), the function See ExamplesFeb 11, 19 · Copy to Clipboard if you want to calculate log (19) and x=09 then you have apply taylor series log (1x) see formula form google and change in to the code is function series_sum=talor (x) %give x=09 as input target_equation = log (1x);



Maclaurin Series For Ln 1 X Youtube


Expand Log 1 E X In Ascending Powers Of X Up To The Term Containing X 4 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
% for calculating log (19) series_sum = 0;Example 74 Consider the geometric series 1 z z2 z3 The limit of the nth roots of the terms is L= lim n!1 jznj1=n= limjzj= jzj Happily, the root test agrees that the geometric series converges when jzjWhat do you get when you plug a in?



Solved 2 A 10 Points Obtain Taylor S Series For The Chegg Com



Taylor Series Theorem Definition The Series Is Called The Taylor Series Of F About C Centered At C Ppt Download
X a 3 is called the Taylor Seriesof f centered at a> 1 Taylor polynomials > 11 The Taylor polynomial Let f(x) be a given function, for example ex,sinx,log(x) The Taylor polynomial mimics the behavior of f(x) near x= a T(x) ≈f(x), for all x"close" to a Example Find a linear polynomial p 1(x) for which ˆ p 1(a) = f(a), p0 1 (a) = f0(a) p 1 is uniquely given by p 1(x) = f(a)(x−a)f0The sine function y with only first three terms can be written as x² x² y = x 2 3 A (5 points) Write a user defined function (UDF), named as simple, with one input x;



Series Expansion Calculator Wolfram Alpha



Taylor Series Wikipedia
Free Taylor Series calculator Find the Taylor series representation of functions stepbystep This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience By using this website, you agree to our Cookie Policy \log 1 2 3\pi e x^{\square} 0 \bold{=} Go Related » Graph » Number Line » Examples » Correct Answer )Apr 15, 18 · 1 Taylor Series By M Bourne Our aim is to find a polynomial that gives us a good approximation to some function (See why we want to do this in the Introduction) We find the desired polynomial approximation using the Taylor Series If we want a good approximation to the function in the region near `x = a`, we need to find the first, second, third (and so on) derivativesI am taking a MATLAB class and the instructions given to run a taylor series example test run is not working To get the Taylor Polynomial of Degree 5 >> syms f x p5



Finding The Natural Logarithm Of A Number Using Taylor Series In C Stack Overflow



Show That Frac 1 2 0 5 Frac 1 Frac 1 2 3 0 5 2 Frac 1 Frac 1 2 Frac 1 3 4 0 5 3 Cdots Log 2 2 Mathematics Stack Exchange
Integral Calculator computes an indefinite integral (antiderivative) of a function with respect to a given variable using analytical integration It also allows to draw graphs of the function and its integral Please remember that the computed indefinite integral belongs to a class of functions F(x)C, where C is an arbitrary constantCommonly Used Taylor Series series when is valid/true 1 1 x = 1 x x2 x3 x4 note this is the geometric series just think of x as r = X1 n=0 xn x 2( 1;1) ex = 1 x x2 2!Dec 21, · Earlier this semester, we saw how to approximate a function \(f (x, y)\) by a linear function, that is, by its tangent plane The tangent plane equation just happens to be the \(1^{\text{st}}\)degree Taylor Polynomial of \(f\) at \((x, y)\), as the tangent line equation was the \(1^{\text{st}}\)degree Taylor Polynomial of a function \(f(x)\)



Taylor Series Wikipedia



Taylor Series Natural Log Page 1 Line 17qq Com
Our next example is the Taylor's series for 1 1 x;Eg, since 1000 = 10 × 10 × 10 = 10 3, the "logarithm baseWhat is the Lagrange remainder for a ln(1x) Taylor series?



The Natural Logarithm And Its Series Expansion 2 Ways Ln X 1 At 0 Youtube



Expand 1 Dim Vector By Using Taylor Series Of Log 1 E X In Python Stack Overflow
This series was first described by Isaac Newton Remember the formula for the geometric series 1 − 1 x = 1 x x 2 x 3 ··· if x < 1 If we replace x by −x we get 1 1 x = 1 − x x 2 − x 3 ··· R = 1 You may recall that the graph of this function has an infiniteThe begin of the quotient series is tanh x = x1 3 x 3 2 15 x 517 315 x 7This seems to work well over most of the domain of log(x), but as x approaches 1 (and log(x) approaches 0) the transformation provided by x = m * 2 e actually produces a less accurate result So a better algorithm would first check if x is close to 1, say abs(x1) < 5, and if so the just compute the taylor series approximation directly on x



Taylor Series Wikipedia



Taylor Series Expansions Of Exponential Functions
Sep 03, 19 · Taylor series of log(x) with a = 1 Follow 54 views (last 30 days) Show older comments Ibrahima Diallo on 3 Sep 19 Vote 0 ⋮ Vote 0 Answered Kritika Bansal on 13 Sep 19 How to Write a Matlab function that sums up a specified number of terms from the Taylor series of log(x) with a = 1Which function is represented by the series 1/n x n Multiplication Multiply two known series together until a pattern emerges Find the Taylor series centered at zero for f(x) = x 2 e 2x Find the first 3 terms of the Taylor series centered at zero for g(x) = sin(2x) e x 2The result 70 is the same as the result we calculated when we wrote out each term of the Taylor Series individually An advantage of using a for loop is that we can easily increase the number of terms If we increase the number of times the for loop runs, we increase the number of terms in the Taylor Series expansion Let's try 10 terms Note how the line for i in range(10) now includes 10


Maclaurin And Taylor Series Power Series Expansion Of Logarithmic Function



Solved The Maclaurin Series Expansion For The Natural Log Chegg Com
= X1 n=0 xn n!Topic Finding the Taylor Series of the Log(1x) or Log(1x) using the Geometric Series What you should know?Expansions Which Have LogarithmBased Equivalents Summantion Expansion Equivalent Value Comments x n



Expand 1 Dim Vector By Using Taylor Series Of Log 1 E X In Python Stack Overflow



Taylor Series Of A Log Function Page 1 Line 17qq Com
Oct 09, 19 · A Taylor series provides us a polynomial approximation of a function centered around point a Because the behavior of polynomials can be easier to understand than functions such as sin(x), we can use a Taylor series to help in solving differential equations, infinite sums, and advanced physics problemsSo e = 1 1 1 2!Taylor series of hyperbolic functions The differentiation rules d d (1);



Why Is It That Natural Log Changes Are Percentage Changes What Is About Logs That Makes This So Cross Validated



Log Taylor Series Page 1 Line 17qq Com
In mathematics, the logarithm is the inverse function to exponentiationThat means the logarithm of a given number x is the exponent to which another fixed number, the base b, must be raised, to produce that number xIn the simplest case, the logarithm counts the number of occurrences of the same factor in repeated multiplication;Chapter 4 Taylor Series 17 same derivative at that point a and also the same second derivative there We do both at once and define the second degree Taylor Polynomial for f (x) near the point x = a f (x) ≈ P 2(x) = f (a) f (a)(x −a) f (a) 2 (x −a)2 Check that P 2(x) has the same first and second derivative that f (x) does at the point x = a 43 Higher Order Taylor PolynomialsI need to nonlinearly expand on each pixel value from 1 dim pixel vector with taylor series expansion of specific nonlinear function (e^x or log(x) or log(1e^x)), but my current implementation is not right to me at least based on taylor series conceptsThe basic intuition behind is taking pixel array as input neurons for a CNN model where each pixel should be non



Solved 1 Use A Taylor Series To Get The Limit 7 4 X2 Chegg Com


What Is The Expansion Of Log 1 X Quora
Jan 28, 16 · How can you find the taylor expansion of #ln(1x)# about x=0?This is known as the Maclaurin series Example Maclaurin series of 1/(1x) is given by 1xx 2 x 3 x 4 , Applications of Taylor Series The uses of the Taylor series areJun 19, 19 · Hi, I was trying to solve the following problem myself but couldn't figure out how the given Taylor series for log(x) is found Taylor series for a function f(x) is given as follows Question 1 I was trying to find the derivative of log(x) My calculator gives it as



Approximating Sine X With A Taylor Series In C And Having A Lot Of Problems Stack Overflow



Solved E An I 3 2 A 2 6 6 Taylor Series 422 Write Chegg Com
And the corresponding Taylor series for log(x) at a = 1 is and more generally, the corresponding Taylor series for log(x) at some is The Taylor series for the exponential function ex at a = 0 is The above expansion holds because the derivative of e xwith respect to x is also e and e0Hi!Learn to find the series expansion of log(1x) and log(1x) hereApr 23, 21 · I know how to find Taylor Series of ) ln(x) about x=2 but the question wants me to find Taylor Series of ) ln(2 x) about x = 2, and nothing works Help pls calculus sequencesandseries powerseries


Taylor Series For Log X Physics Forums



The Taylor Series And Machine Learning James D Mccaffrey
Get the free "Log(1x) Taylor Series" widget for your website, blog, Wordpress, Blogger, or iGoogle Find more Mathematics widgets in WolframAlphaGeometric Series Integration of power functIf you know Lagrange's form of the remainder you should not need to ask Also you haven't said what point you are expanding the function about (although it must be greater than math0/m



Taylor Series For Ln 1 X How To Steps Math Class 21 Video Study Com



Taylor Series For F X Ln X Centered At X 1 Youtube
With one swift use of the power rule, we were able to generate a Taylor series for 1 (1 − x) 2 \dfrac{1}{(1 x)^2} (1 − x) 2 1 Pretty amazing!Question points) The Taylor series of In(1x) at x = 0 is In(1x) = (1)*1 xk n ke1 You are asked to evaluate the accuracy of the Taylor series when only finiteTaylor expansion of 1 x The Taylor series for f Table 1 Taylor Series for f (x) = 1 x The general coefficient of the expansion, for n


Taylor Series For Log X Physics Forums



Taylor Series Wikipedia
How do you expand log 1log (1x) in powers of x as far as x^4?
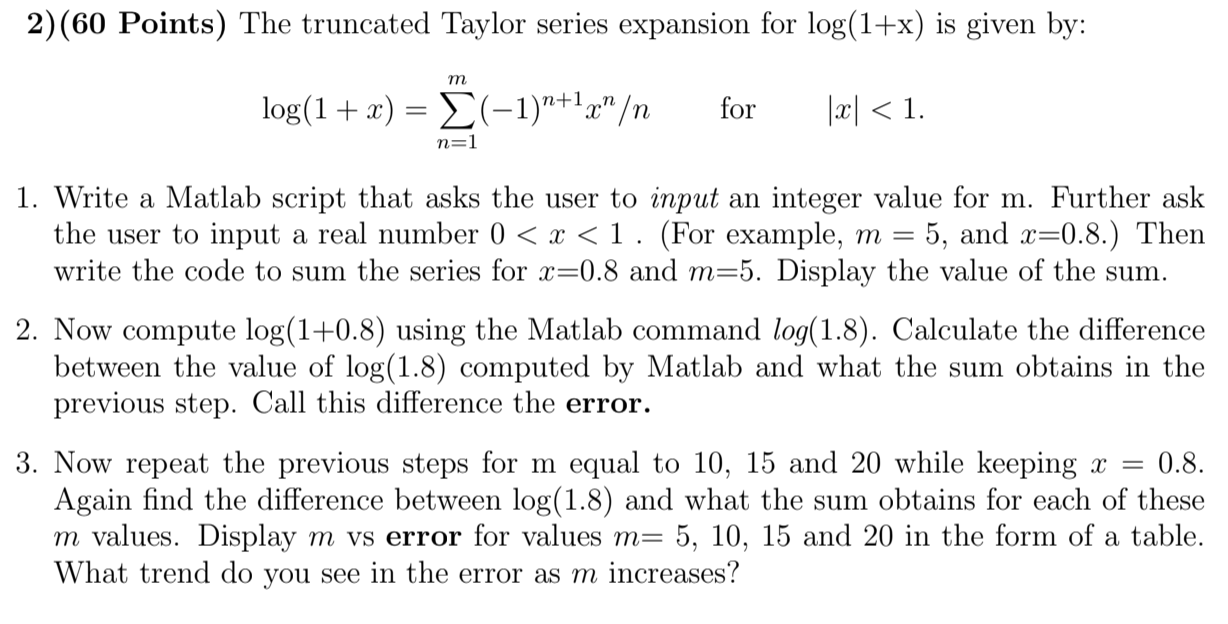


Solved 2 60 Points The Truncated Taylor Series Expansio Chegg Com



Math Review With Matlab Calculus Taylors Series S



Thermodynamics 17 Taylor Expansion Ln 1 X Youtube



Taylor Expansion Of Log X Page 1 Line 17qq Com



What Is The Taylor Series Expansion Of 1 Log X About X 2 Quora



Natural Logarithm Wikipedia


How Do You Find The Maclaurin Series For F X Ln Cosx Socratic



Solved 7 The Taylor Series Approximation For Log 1 Z Chegg Com



F A X 4 Expand The Following Functions In A Maclaurin Series 2 1 X B 1 Homeworklib



Taylor Series Wikipedia



Consider The Following Two Taylor S Series Log 1 Chegg Com



How To Find The Maclaurin Series Of 1 1 X 2 Youtube


Introduction To Taylor S Theorem For Multivariable Functions Math Insight



Taylor Series Expansions Of Logarimathic Functions


What Is The Taylor Series Expansion Of Sin X Quora


Cochranmath Taylor Series Integration And Differentiation



What Is The General Term For E X 1 X Mathematics Stack Exchange
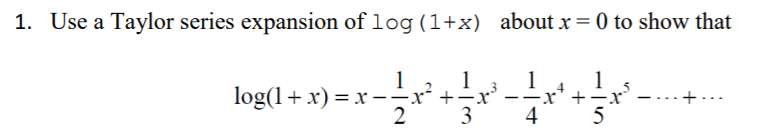


Solved 1 Use Taylor Series Expansion Log 1 X Aboutx 0 Show Q



Logarithms Logs Log Ln Lg


Expand Tan 1y X About The Point 1 1 Using Taylor S Theorem Up To The Second Degree Terms Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community


Expand Tan 1y X About The Point 1 1 Using Taylor S Theorem Up To The Second Degree Terms Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



Taylor Series With Python And Sympy Revised R Craft



Solved 18 5 Pts Taylor Series Approximation Log 1 X Log Natural Logarithm 3 2 73 4 Log 1 X X Unl Q 1



Taylor Series Wikipedia



Taylor Series Wikipedia


Maclaurin And Taylor Series Power Series Expansion Of Logarithmic Function



Expand The Function F Z Log 1 Z 1 Z In Taylor Series Homeworklib



Taylor Series Numerical Methods Projects



Expand Logex In Power Of X And Hence Evaluate Loge 1 1 Correct To Four Decimal Places Answer Mathematics 1 Question Answer Collection



Some Wolfram Alpha Features I Can T Achieve In Mathematica Mathematica Stack Exchange



Taylor Series



Solved Find The Following Limit Lim X Rightarrow 0 Ln 1 X X X 2 1 Answer Transtutors


Expand Log 1 Sinx Up To The Term Containing X 4 By Using Maclaurin S Theorem Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



Help With Arithmetic On Basic Taylor Series Expansion Mathematics Stack Exchange



Natural Logarithm Wikipedia



通过使用python中的log 1 E X 的taylor级数展开1个暗淡矢量


Taylor Series
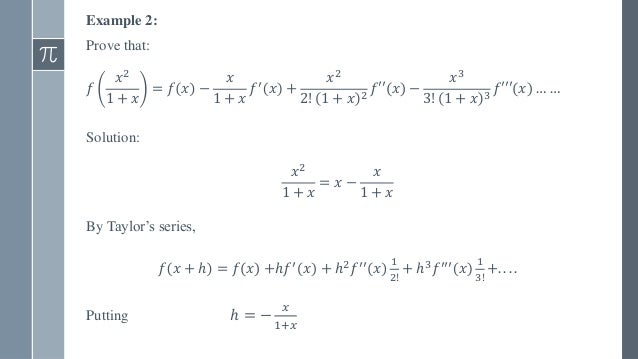


Power Series Taylor S And Maclaurin S Series



Why Is It That Natural Log Changes Are Percentage Changes What Is About Logs That Makes This So Cross Validated
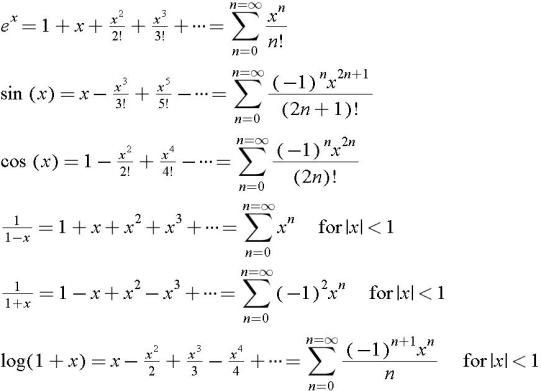


Appendix C Expansions Differentiation Integrals And Mathematical Relations Engineering360



Taylor Series Wikipedia


Series Wolfram Language Documentation



Taylor Series Wikipedia


Maclaurin And Taylor Series Power Series Expansion Of Logarithmic Function



What Is The Correct Radius Of Convergence For Ln 1 X Mathematics Stack Exchange


Write Down The Taylor Series Expansion Of The Function Log X About X 1 Upto Three Non Zero Terms For X 0 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community


Natural Logarithm Series
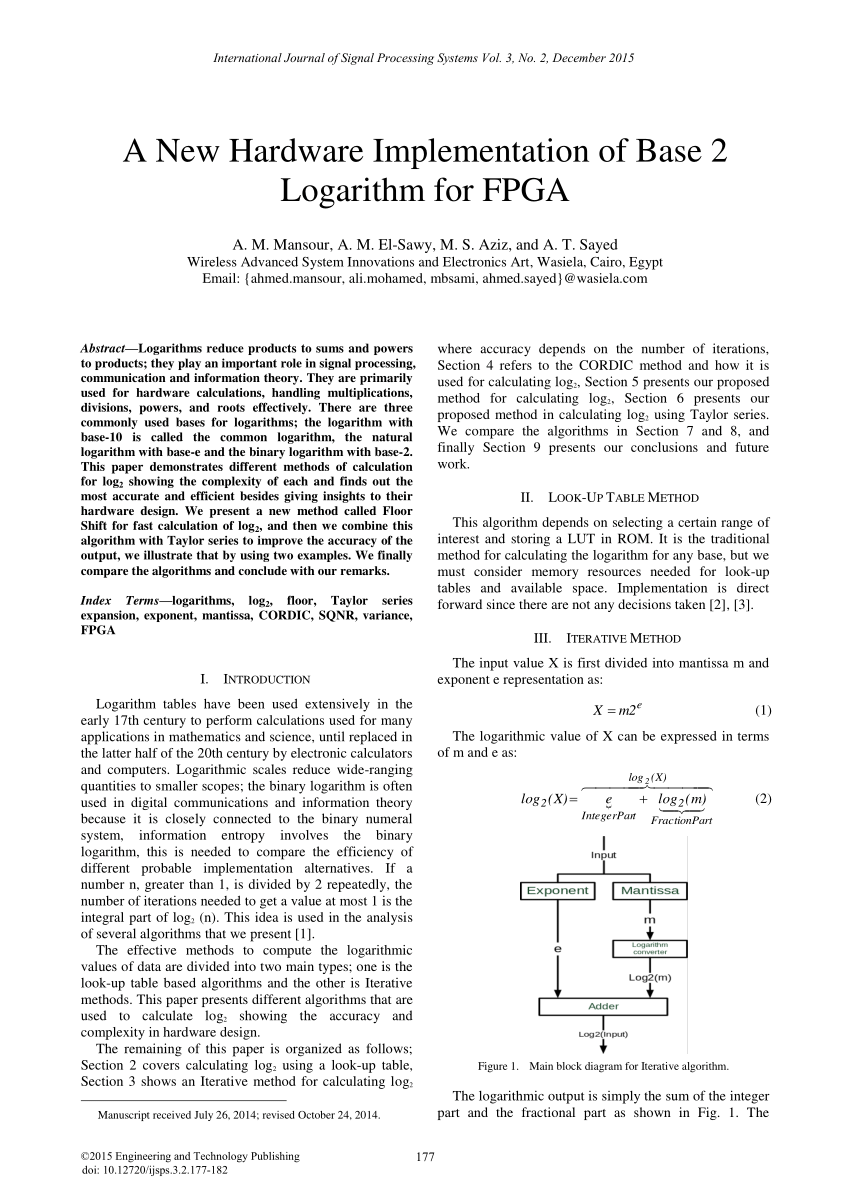


Pdf A New Hardware Implementation Of Base 2 Logarithm For Fpga



Numerical Integration Error For Simpson S Rule Through Taylor Series Mathematics Stack Exchange



Graphs Of Taylor Polynomials Wolfram Demonstrations Project



Log 1 E X Maclaurin Series



Natural Logarithm Wikipedia


Natural Logarithm Series
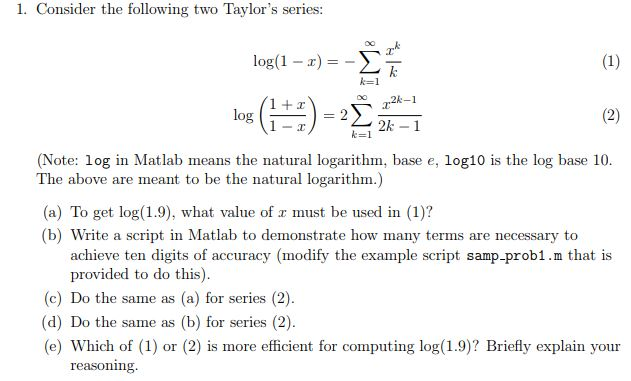


Solved 1 Consider The Following Two Taylor S Series Log Chegg Com



Taylor Series For The Natural Logarithm F X Ln 1 X Youtube



Taylor Series Wikipedia


Maclaurin Series Of E Sinx



Taylor Series Wikipedia



File Matlablog 1 X Png Wikiversity


コメント
コメントを投稿